For the reason which is about 100 micrometers, Thin Crystal polarizer(TCP) can be used even place (which does not have the spaces under an object lens, etc. ).
This product is manufactured with custom-made.
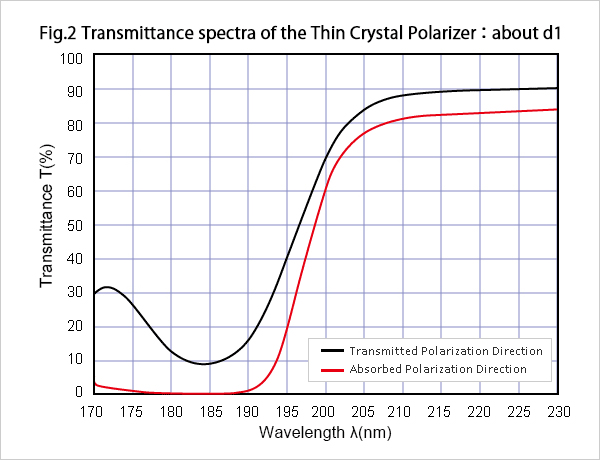
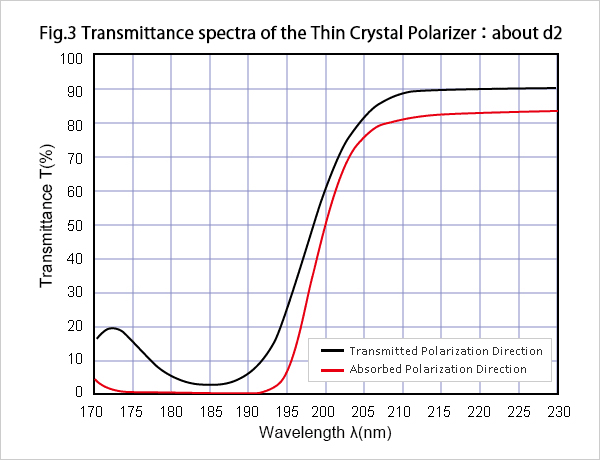
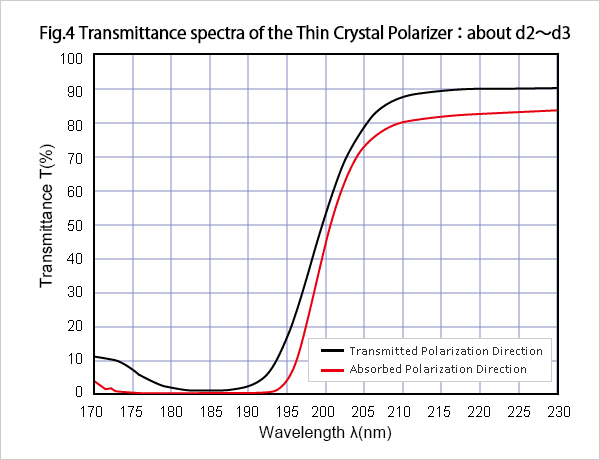
Although TCP is the light polarizer for wavelength λ=193nm, but it can mainly be used on other wavelengths, such as λ= 175 nm or λ= 185 nm, because it has the characteristic shown in Fig.2~4.
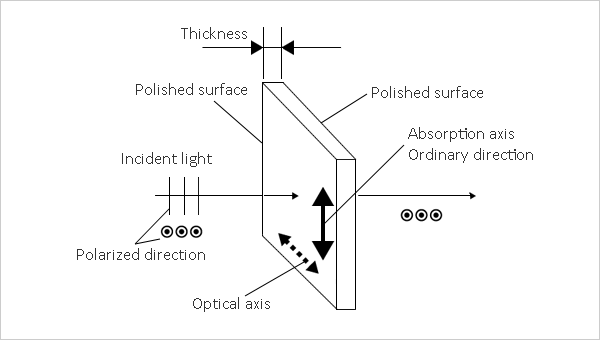
Schematic diagram of the Thin Crystal Polarizer is shown in Fig.1.
This polarizer consists of a thin uniaxial crystal, in which the absorption coefficient of ordinary ray is different from absorption coefficient of extraordinary ray at λ=193nm.
The absorption coefficient for ordinary ray is larger than for extraordinary ray.
Therefore the transmittance for extraordinary ray is larger than for ordinary ray.
The Thin Crystal Polarizer is a variety of dichroism polarizer.
Schematic diagram of the Thin Crystal Polarizer
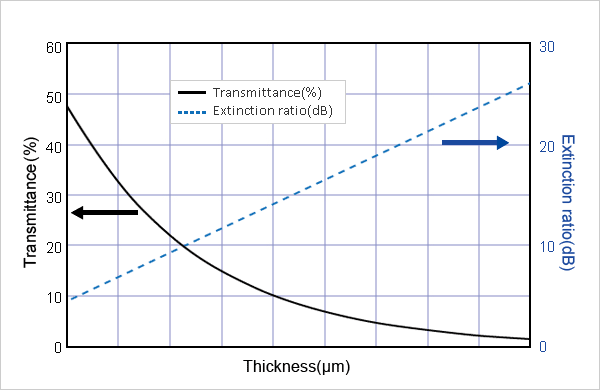
Typical properties of the Thin Crystal Polarizer are shown in Table 1.
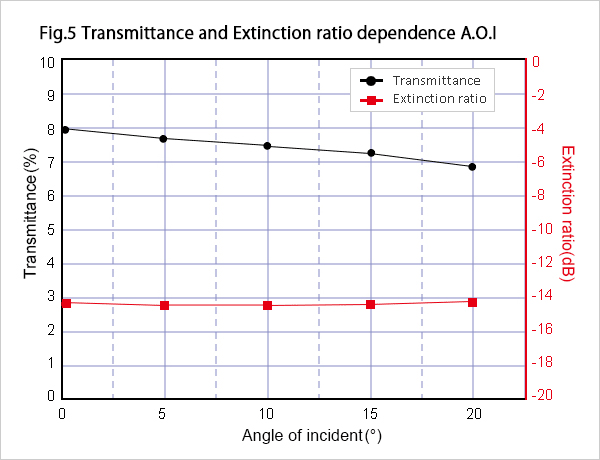
The measurement example of an incidence angle versus transmittance and an Extinction ratio is shown in Fig.5.
Transmittance and extinction ratio have little change by incidence angle change.
Specifications
Table 1 Transmittance and extinction ratio for Thin Crystal Polarizer| thickness | Transmittance(℅) | Extinction ratio(dB) |
| d1 | 26 | 8 |
| d2 | 17 | 10 |
| d3 | 4 | 20 |
at λ=193nm